안 써본 사람은 있어도, 한 번만 써본 사람은 없다는 Visual Assist.
MS사의 Visual Studio 제품군을 이용한다면 한번씩은 들어봤을 터이고, 사용해봤을 범한 편리한 툴이다.
C#에서는 사용빈도가 높진 않지만 C++쪽에서는 은근 사용빈도가 높아 정리를 해보았다.
자주쓰는 단축키는 공식홈페이지의 문서에서 참조하여 정리하였다.
단축키는 기본 설정값 기준이다.
| 명령 | 설명 | 단축키 |
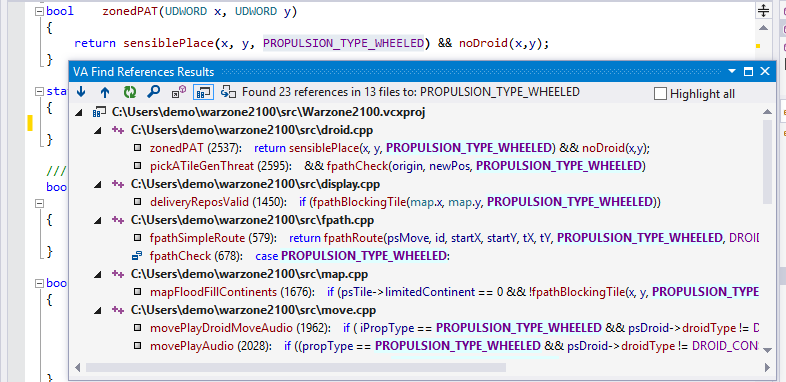
| 참조 찾기 (FindReferences) |
현재 커서에 선택된 변수/함수가 참조되는곳 모두 찾기 | Shift+Alt+F |
| 심볼 찾기 (FindSymbolDialog) |
대화상자가 나타나며, 키워드를 포함하는 현재 솔루션내 존재하는 심볼 나열 | Shift+Alt+S |
| 정의로 이동 (GotoImplementation) |
현재 커서에 선택된 변수/함수 정의로 이동 | Alt+G |
| 헤더/소스 파일 전환 (OpenCorrespondingFile) |
현재 문서의 헤더/소스 파일로 전환 | Alt+O |
| 파일 찾기 (OpenFileInSolutionDialog) |
대화상자가 나타나며, 키워드를 포함하는 현재 솔루션 내 존재하는 파일 나열 | Shift+Alt+O |
| 리펙터 네이빙 변경 (RefactorRename) |
현재 커서에 선택된 변수/함수의 네이밍 변경 대화상자. (한번에 해당 변수/함수의 이름을 바꿀수 있어 유용) |
Shift+Alt+R |
| 스마트 선택영역 확장 (SmartSelectExtend) |
현재 커서를 기준으로 여러번 누를시 선택영역 범위를 점차 늘림 (단어->문장->문단->블럭 순) | Shift+Alt+] |
| 스마트 블럭 선택영역 확장 (SmartSelectExtendBlock) |
현재 커서를 기준으로 여러번 누를시 선택영역 범위를 블럭 단위로 늘림 | Alt+] |
| 스마트 선택영역 축소 (SmartSelectShrink) |
위의 SmartSelectExtend와 반대되는 기능 선택 영역 범위를 점차 줄임 |
Shift+Alt+[ |
| 스마트 블럭 선택영역 축소 (SmartSelectShrinkBlock) |
위의 SmartSelectExtendBlock와 반대되는 기능 선택영역 범위를 블럭단위로 줄임 |
Alt+[ |
'Programming' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [쉘스크립트] 파일명에서 특정 키워드 일괄 삭제하기 (0) | 2022.05.04 |
|---|---|
| Visual Studio 영문 간격이 이상할때 (0) | 2021.07.19 |
| [C++/MFC] SendMessage 와 PostMessage 차이점 (0) | 2020.07.14 |
| 영문 윈도우에서 VisualStudio 한글이 깨질때 해결방법 (0) | 2019.12.17 |
| [C++] LNK2019 _GetAdaptersInfo@8 Error 관련 (0) | 2019.12.12 |




